Position Interpreters (PIs) Guide
This guide will walk you through building an Position Interpreter. An Position Interpreter is the ruleset that Zapper uses to interpret the value of a position that a user has in a protocol, whether its tokenized or non-tokenized.
Components of a Position Interpreter
This guide assumes that you have already read about what positions are. If you haven't, please read the overview of Positions.
There are 3 key components of an Position Interpreter:
-
Contract Address: The address of the contract the interpreter interprets. This could be 1 contract address you input or a list of contract addresses fetched from a contract factory.
-
Underlying token address: The address of the token that the user deposited into the investment.
- This could be 1 token address you input, or sourced from a method called on the token contract.
- There could also be multiple underlying tokens, such as the case for a pool token, which often has 2 underlying tokens, or a vault, which can have
nunderlying tokens.
-
Price Per Share: The price per share of the position, in terms of how much its worth in terms of the underlying token. This is the value that Zapper uses to calculate the user's balance.
- Sometimes, it's simple, where 1 position is redeemable for 1 underlying token (such as with Aave's aUSDC, where 1 aUSDC = 1 USDC).
- This calculation could also be more complex, such as with Yearn's yCRV, where the price per share is calculated based on the underlying tokens in the vault.
For tokenized postions, note that a user's balance is assumed to be based on a balanceOf method on the token contract. If the token contract does not have a balanceOf method, or the balance returned from that method is not the correct way to fetch a user's balance of the position holding, then it is not an ERC20 token and would not be interpreted as a tokenized position. Instead, this would be a non-tokenized position interpretation.
Position Interpreter walkthrough
Below is a step-by-step guide to creating a Position Interpreter.
Also, check out this video guide to creating an Position Interpreter for tokenized positions:
For more video guides, check out the Learning Center.
1. Create a new Position Interpreter
You can get started by navigating to your Dashboard page and clicking the "Add Balance" button. This will open a modal where you can select the Position Interpreter option.
2. Input the contract address
Input the contract address of the position you want to interpret. This guide will start with a single contract address, but you can also build an interpreter for multiple contract addresses as once using a contract factory. To do do this, see the Position Interpreter Factory Guide for more information.
- A good contract to practice with, that is being used in this guide, is the Compound's cUSDC token. The token address is
0x39AA39c021dfbaE8faC545936693aC917d5E7563on Ethereum mainnet. You'd just paste the sting in to the input box.
2.1 Interpreting multiple contracts from a contract factory
You can interpret many contract positions at once if they are all created from the same contract factory and call the same methods to build their balances. This can be extremely helpful, so you don't have to create an interpreter for each position.
Many protocols leverage contract factories to create their new contracts that hold positions, such as Yearn, SushiSwap, and Uniswap. If you are interpreting a position from one of these protocols, you can likely interpret multiple contracts at once. Often, if an position was created by a factory, it will have a factory method that returns the address of the factory that created it.
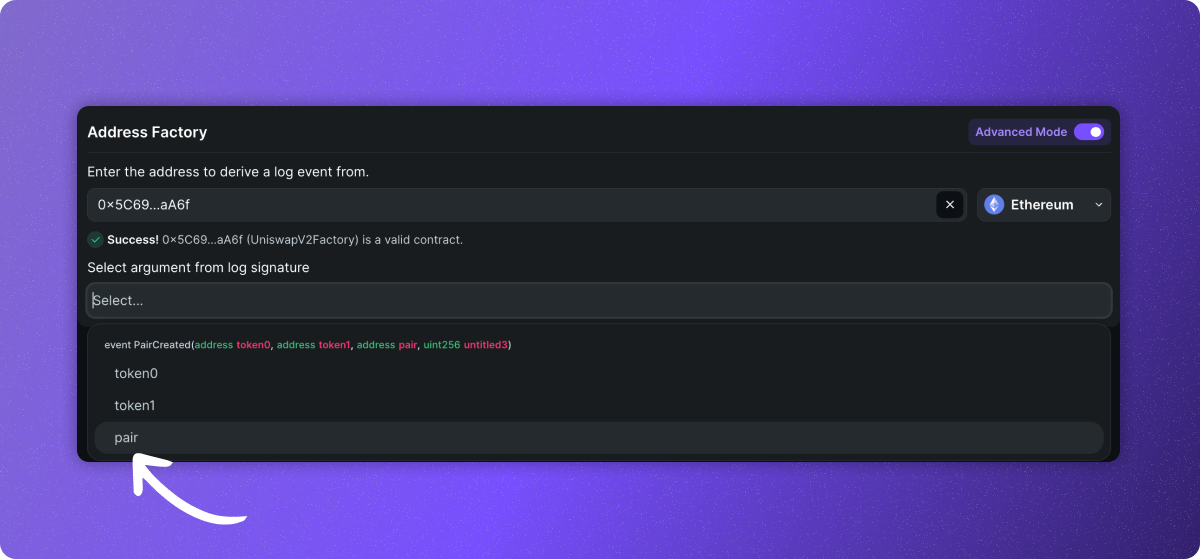
To interpret a contract factory, toggle to choose "Multiple" in the "Are you integrating a single position or multiple positions?" section of the interpreter page.
Next, input the contract factory address in the input box. This will result in Zapper fetching a list of logs that were emitted by the factory contract that contains an address value in output. You can then select the parameter that returns the position address from the logs each time a new contract is created.
To confirm that you chose the correct log, you should see multiple positions in the previewed token price section on the right-hand side. Once this is confirmed as correct, you can go ahead with the rest of the steps as normal to complete the interpreter.
3. Select the chain for the position
Select the chain that the contract is on. This will help Zapper fetch the contract's metadata and balance information.
And with that, you're done with the initial setup! You can now move on to the next steps to complete the interpreter.